管理实际库存结构¶
仓库¶
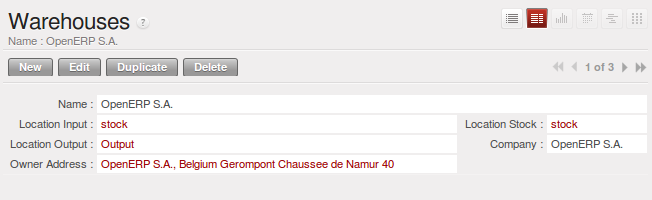
仓库是设计用于向客户进行交付活动或是接收原材料的实际场所。 当你从供应商处购买产品时,你应该考虑这次采购所要使用的仓库。这也使得最终用户不必从库位列表中进行选择,而是一个真实的仓库
使用菜单 , 然后点击新建配置一个新的仓库.
A warehouse is defined by a link between three locations:
- 库位库存 字段显示了可以直接从这个仓库交付给客户的可用的产品. 可用数 给出在这个库位以及子库位的所有产品。
- The Location Input field shows where ordered products are received from a supplier in that warehouse. It can be the same as the stock location if, for example, you want to do a quality control operation on your incoming raw materials.
- The Location Output field (called
Outputin the demonstration database) is designed as a buffer zone in which you store all the items that have been picked, but not yet delivered to a customer. You are strongly advised not to put this location within the stock hierarchy but instead at a higher level or at the same level.
你也能为仓库设置一个地址。这个地址应该是你的公司的一个地址。一旦仓库被定义,你能用在:
- 最小库存规则,
- 供应商订单,
- 客户订单 (用在 POS的定义,关联到一个仓库).
自动产生需求¶
OpenERP 有多种自动供应(procurement)产品的方法:
- the workflow used by products that have the procurement method Make to Order,
- 对于*Make to Stock*产品(存货制造),可以使用最小库存规则
- 对于*Make to Stock*产品(存货制造),使用主生产计划(Master Production Schedule)
The last two methods are described below.
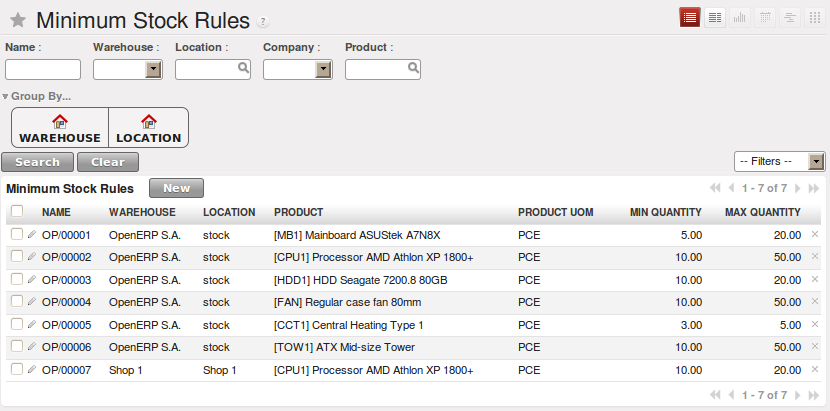
最小库存规则¶
当希望自动产生补货请求是,你可以使用最小库存规则. 菜单路径: .
规则如下:如果指定地点(location)的虚拟库存(virtual stock)比规则中指定的最小库存量少, 系统会自动建议采购,增加虚拟库存(virtual stock)的数量至规则中规定的最大值
Tip
Conflict Resolution
You may find draft production or procurement orders to be created although they should not exist. That can happen if the system is badly configured (for example, if you have forgotten to set the supplier on a product).
To check this, look at the list of procurements in the exception state in the menu . More details about processing these exceptions is given in ch-mnf.
We underline that the rule is based on virtual quantities and not just on real quantities. It takes into account the calculation of orders and receipts to come.
如下面的例子:
- 库存中的产品数量:15
- 已下单(Sales Order?)但是未发货的数量:5
- 在制数量:2
定义的规则为:
- 最小库存: 13
- 最大库存: 25.
一旦规则被正确设置,采购经理只需要查看订单(采购订单)列表与供应商进行确认,菜单路径为 .
Note
Procurement
注意,供应请求不一定要求你从供应商处购买,如果产品有一个属性
Supply Method Produce,(注:即供应方式为生产)
主生产计划(scheduler)会产生一个生产工单,而不是一个采购订单
你也可以在规则中设置最小包装量(multiple quantities). 如果你设置的最小包装量为3,系统会建议一个15pieces的供应, 而不是真正需要的13。在这种情况下,系统会自动根据最小包装量取上整数。(注:即根据最小包装取整,多买一个最小包装的量)
Note
Maximum Quantity
注意一个事实,最大数量不是你库存的最大量。 比如:一个公司有10 pieces的产品,最小库存规则设置为,最小数量 = 10, 最大数量 = 30 及 最小包装 = 12 如果有一个预计的2 piece订单(销售订单),系统执行计算后会产生一个24 pieces的采购需求。 第一个12 pieces会用于达到最小数量,第二个12 pieces用于达到最大数量。
In a minimum stock rule, when you indicate a warehouse, it suggests a stock location by default in that warehouse. You can change that default location when the scheduler completes.
库位¶
一个库位(或 货位)是仓库中的一个组成部分,用来管理所有类型的库存位置。 such as at the customer’s and production counterparts.
根据你的需求,在你(在系统中)构建你的仓库时候,可以设置不同类型的库位。 Locations are structured hierarchically to account for the subdivision of a warehouse into sections, aisles, and/or cupboards. (译:库位是多层级结构的,用于将仓库分为更小的子层级,如 区域、通道 或者 cupboards(货架?)) The hierarchical view also enables you to structure virtual locations such as production counterparts. That gives you a finer level of analysis. Go to the menu , then click New to define new locations.
下面是几种常见的库位:
供应商库位: 虚拟货位,代表产品是从供应商处接收的(如收货时候,源货位就是供应商货位,代表供应商库存减少)
视图库位: shows that the location is only an organizational node for the hierarchical structure, and cannot be involved in stock moves itself. The view type is not made into a leaf node in a structure – it usually has children.内部库位: 您仓库中的物理货位客户库位: 虚拟货位,表示货物发送给了客户,(如销售订单发货后,客户货位增加,表示已经发给了客户)盘点/损耗库位: virtual location serving as the counterpart for inventory operations used to correct stock levels (physical inventories),Procurement: virtual location serving as temporary counterpart for procurement operations when you do not yet know the source (supplier or production). Products in this location should be zero after the scheduler run completes,生产库位: 生产过程的虚拟货位,用来记录原材料消耗(发放至此货位)以及成品完工来源多公司间中转库位: 用于多组织环境中的中间过程货位。(如两个组织间调拨时候,货物仍在途的情况)
You can have several locations of the same type. In that case, your product, supplier and warehouse configurations determine the location that is to be used for any given operation.
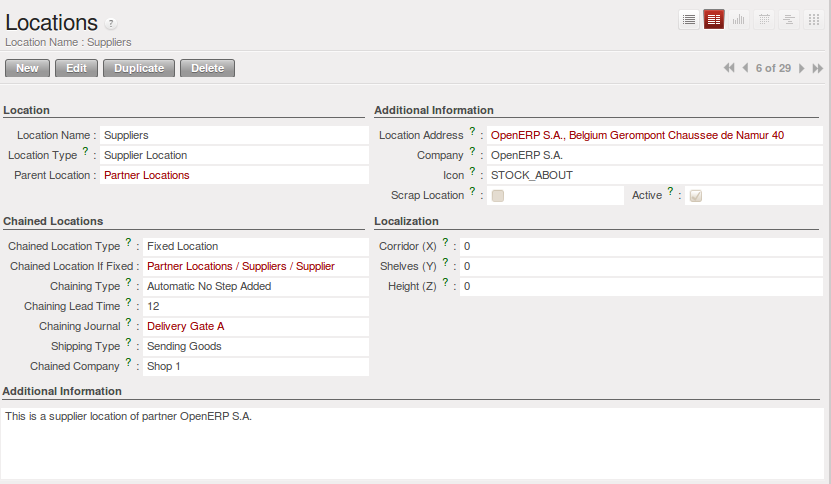
库位地址¶
每个库位可以指定一个地址,使你能够给客户或者供应商建立一个库位。 如:你能够设置库位地址为供应商或者客户的地址。 去 业务合作伙伴 界面,告诉OpenERP,他应该使用这个库位,而不是默认库位 (Go to the partner form to tell OpenERP it should use this location rather than the default location given to partner deliveries.)
Tip
Subcontracting Production
You will see in the on line chapter Manufacturing that it is possible to assign a location to a manufacturing workcenter. If this location is at a suppliers, you must give it an address so that OpenERP can prepare a delivery order for the supplier and a receive operation for the manufactured goods. Creating a location specifically for a partner is also a simple solution for handling consigned stocks in OpenERP.
Note
托管库存(Consigned Stock)
Consigned stock is stock that is owned by you (valued in your accounts), but is physically stocked by your supplier. Or, conversely, it could be stock owned by your customer (not valued by you), but stocked in your company. Make sure that you create consignment locations as part of your internal stock.
To enable you to easily consolidate at a higher level, the location definition is hierarchical. This structure is
given by the field Parent Location. That also enables you to manage complex cases of product localization.
例如,你可以想象一下以下场景:一个公司有两个仓库
一个公司有两个仓库,一个在巴黎,一个在波尔多。对于某些销售订单,你需要从巴黎发货,另外一些订单需要由波尔多进行发货。 但你仍需要指定一个虚拟的仓库给OpenERP,让系统计算他应该由巴黎还是波尔多进行发货。 在OpenERP里面,你可以设置一个(虚拟)仓库“法国”,组合(consolidates)了巴黎仓库和波尔多仓库。 (注:也就是设定了 法国.巴黎,以及 法国.波尔多 ?) 你建立了以下物理库位:
- Company
- Output
- Warehouses France
- Warehouse Paris
- Warehouse Bordeaux
- Warehouses France
- Output
OpenERP会从有产品库存的仓库发货。 当产品在几个仓库均有货时,OpenERP会选择最近的仓库(进行发货)。 为了让系统知道仓库之间的距离,你需要为每个仓库设置地理坐标(X,Y,Z),以便OpenERP搜索最近的货物。 同样,坐标可以用于构建仓库的货架、货道和内部房间。(注:即仓库内部坐标)
链式库位¶
OpenERP中的库位是可以相互链接在一起,以定义产品的路径的。 因此你能够定义如下规则:所有进入仓库的产品会自动的发送至质量监控(即检验货位)。 仓储和质检由两个不同的货位表示(即类似于收货时,在一个货位做质检,另外一个货位做储存)
这样,当一个货物到达库位时候,OpenERP会自动建议你将货物发送到一个链接的库位。 有3种链接的模式:
- 手工操作(Manual Operation),
- 自动移动(Automatic Move),
- 自动无步骤添加(Automatic No Step Added).
手工操作 模式,一旦货物到达源库位,(系统)会创建一张内部物料搬运单(从当前库位)至链接库位 物料搬运单会等待用户的确认(confirmation of the move)。 This enables you to have a list of moves to do, 物料搬运单由系统建议,由仓管员(storesperson)确认。
自动移动(Automatic Move) 模式会做相同的事情,但不会等待一个用户的确认(即移动步骤系统自动完成了)。 不需要人工的接入,产品会自动发送到链接库位。 这适合于,为了简化操作,你删除了系统上的一个操作步骤,用户自己完成这个(物理的)操作流程。 (即系统上少操作一步,但是现实中库存人员还是做了两步,如检验-入库)
自动无步骤添加(Automatic No Step Added) 模式不会包含额外的库存移动,但会透明的将目标库位进行更改至链接库位。(即直接更改目标库位,不会产生上面两个模式中的物料搬运单) You could then assign a destination location to which you send all the products that arrive in your warehouse. The storesperson will modify the goods receipt note.
Tip
Product Logistics
The module stock_location lets you generate paths to follow, not just at the level of locations, but also at the
level of products. It then enables you to manage default locations for a given product or to refer to the products
as a function of operations such as quality control, supplier receipt, and after-sales service.
A more detailed explanation of this module, with examples, is given at the end of this chapter.
If there is linking to do, the Chained Location Type field allows you to determine the destination location. If the field is set to ‘Customer’, the location is given by the properties of the partner form. If the field is set to fixed, the destination location is given by the field Chained Location If Fixed.
Some operations take a certain time between order and execution. To account for this lead time, you can set a value in days in the field Chaining Lead Time. Then the extra move (automatic or not) will be carried out several days after the original move. If you use the mode Automatic No Step Added, the lead time is inserted directly into the initial order. In this way, you can add security lead times at certain control points in the warehouse.
结构化库位¶
In the next part, you will see that by linking locations you can manage a whole series of complex cases for efficient production management:
- Handling multiple operations for a customer order,
- Tracking import and export by sea transport,
- Managing a production chain in detail,
- Managing rented products,
- Managing consigned products.
To show these concepts, different cases of structuring and configuring these locations are given below. Many other configurations are possible according to company needs.
Examples:
- Handling customer orders
Customer orders are usually handled in one of two ways:
- item note (or preparation order), confirmed when the item is ready to send,
- delivery order (or freight note), confirmed when the transporter has delivered the item to a customer.
You use the following stock move in OpenERP to simulate these operations:
- Packing Note: Stock > Output,
- Delivery Order: Output > Customer.
The first operation is automatically generated by the customer order. The second one is generated by the stock management, showing that the Output location is linked to the Customer location. The two operations will be displayed in Waiting status. If the Output location is not situated beneath the stock location, you then have to move the item from stock to the place where the item is prepared.
Some companies do not want to work in two steps, because it just seems like extra work to have to confirm a delivery note in the system. You can then set the link mode to ‘Automatic’ to make OpenERP automatically confirm the second step. It is then assumed all the items have automatically been delivered to the customer.
- Linked production
The stock_location module enables you to manage the linkages by product in addition to doing that by
location. You can then create a location structure that represents your production chain by product.
The location structure may look like this:
Stock
Level 1
Level 2
- Link 1
- Operation 1
- Operation 2
- Operation 3
- Operation 4
- Link 1
You can then set the locations a product or a routing must go through in the relevant form. All products that enter the production chain will automatically follow the predetermined path. You can see the location structure using .
商店¶
The counterparts for procurement, inventory and production operations are given by the locations shown in the product form. The counterparts of reception and delivery operations are given by the locations shown in the partner form. The choice of stock location is determined by the configuration of the warehouse, linked to a Shop, which can be defined using .
Once a shop is defined, you will be able to make sales orders from this shop. You need at least one shop in order to be able to make sales orders.
库存¶
In the Product form, the Stock by Location action will give you the stock levels of the various products in any selected location. If you have not selected any location, OpenERP calculates stocks for all of the physical locations. When you are in the Stock by Location view, click the Print button to print the Location Content or the Location Inventory Overview reports.
Note
Availability of Stock
Depending on whether you look at the product from a customer order, or from the menu of a product form, you can get different values for stock availability. If you use the Product menu, you get the stock in all of the physical stock locations. Looking at the product from the order you will only see the report of the warehouse selected in the order.
In this respect, two important fields in the product form are:
- Real Stock: Quantity physically present in your warehouse,
- Virtual Stock: Calculated as follows: real stock – outgoing + incoming.
Note
Virtual Stock
Virtual stock is very useful because it shows what the salespeople can sell. If the virtual stock is higher than the real stock, this means products will be coming in. If virtual stock is smaller than real stock, certain products are reserved for other sales orders or work orders.
Tip
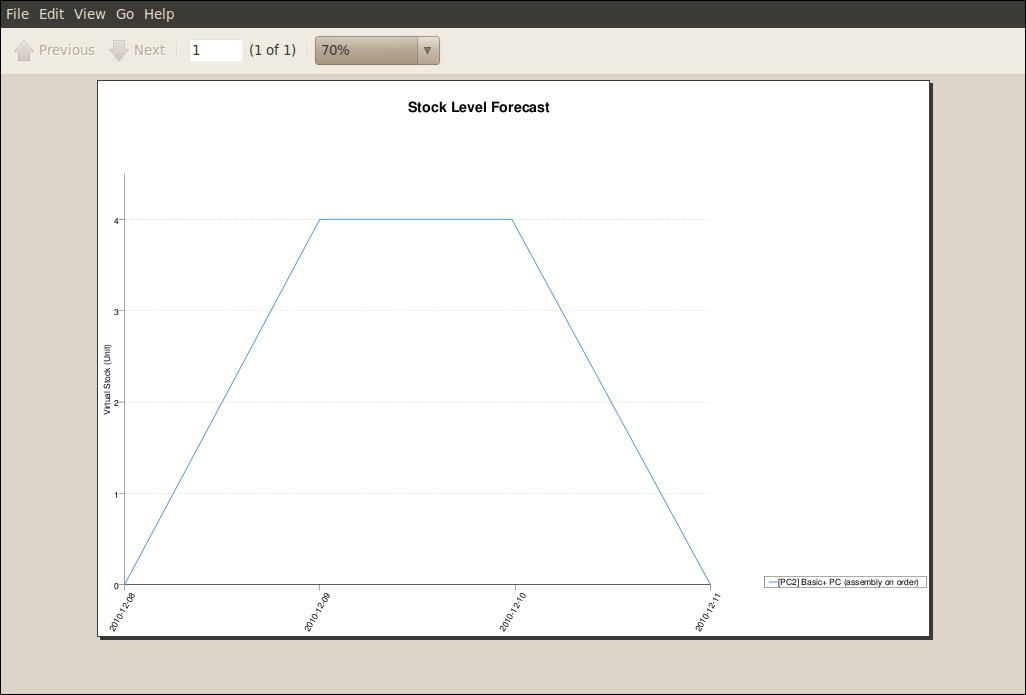
Detail of Future Stock
To get more details about future stock, you can click Stock Level Forecast to the right of the product form to
get the report Forecast Stock Levels as illustrated below. OpenERP shows a graph of the changes in stock
in the days to come, varying as a function of purchase orders, confirmed production and sales orders.
Tip
Filter Stock by Location
By default, in Product list view, the columns Real Stock and Virtual Stock show the stock figures for all stock locations where a product is stored. Use the Extended Filters to enter a specific stock location, if you want to only see the stock in a specific location.
提前期和库位¶
The tab Procurement & Locations in the Product form contains information about different lead times and locations. Three lead time figures are available:
- Customer Lead Time: lead time promised to the customer, expressed in number of days between the order and the delivery to the customer,
- Manufacturing Lead Time: lead time, in days, between a production order and the end of production of the finished product,
- Warranty (months): length of time in months for the warranty of the delivered products.
Note
Warranty
The warranty period is used in the Repairs management and after-sales service. You can find more information on this subject in the on line chapter about Manufacturing.
Fields in the section Storage Localisation are for information only; they do not have any impact on the management of stock.
Counter-Part Locations Properties are automatically proposed by the system, but the different values can be modified. You will find counterpart locations for:
- Procurement,
- Production,
- Inventory.
A procurement location is a temporary location for stock moves that have not yet been finalized by the scheduler. When the system does not yet know if procurement is to be done by a purchase or production, OpenERP uses the counterpart location Procurement. In this location, you will find everything that has not yet been planned by the system. The quantities of product in this location cancel each other out.
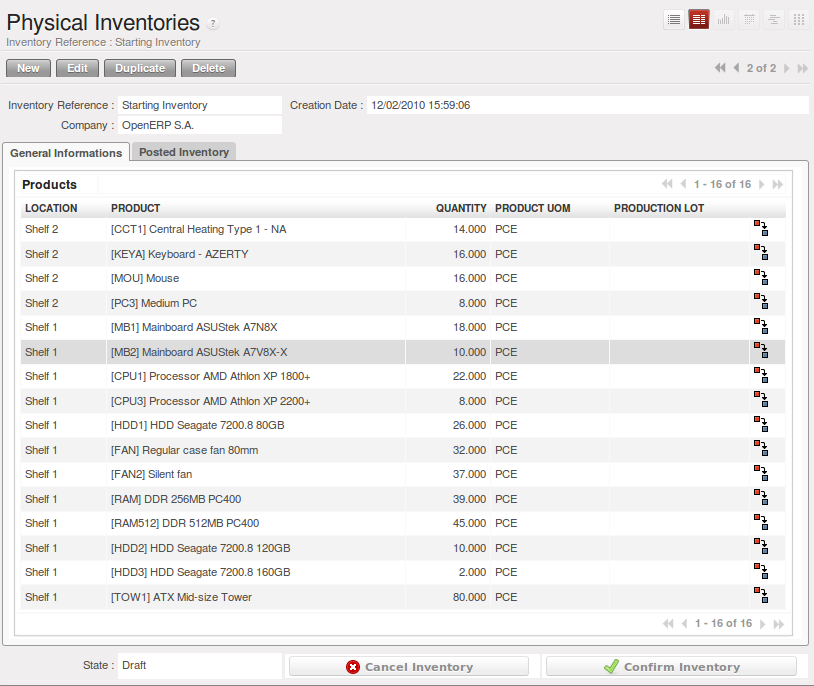
期初库存¶
Once a product has been defined, use an initial inventory operation to put current quantities into the system by location for the products in stock. Go to the menu to do your initial inventory.
Give a name (for example Initial Inventory or Lost Product XYZ) and a date (proposed by default) for each inventory operation.
You have three ways of doing an inventory.
- Click the Import Inventory action and select the location concerned. You can choose to include child locations and set the inventory to zero (especially useful to ensure the count is done correctly).
- You can update the inventory from the Product form. Go to the Information tab, Stocks section, and click the Update button. On confirmation, OpenERP will create a Physical Inventory.
- You can manually add inventory lines. You can then enter data about the quantities available for each product by location. Start by entering the location, for example Stock, and then select the product. OpenERP automatically completes the quantity available for that product in the location shown. You can then change that value to correct the value in stock.
Enter data for a single line in your inventory:
- Location : Stock,
- Product : PC1 Basic PC,
- Quantity : 23 Units.
When your inventory operation is finished, you can confirm it using the Confirm Inventory button to the bottom right of the form. OpenERP will then automatically create the stock moves to close the gaps, as mentioned at the start of this chapter. You can verify the moves generated using the Posted Inventory tab of the inventory operation form.
The correct levels of your product are now in your stock locations. A simple way of verifying this is to reopen the product form to see the quantities available in stock.
Tip
Periodical Inventory
You are usually legally required to do a stock check of all your products at least once a year. As well as doing a complete annual stock check, OpenERP also supports the method of periodical inventory.
That means you can check the stock levels of a proportion of your products every so often. This system is accepted in France as long as you can guarantee that all of your products have been counted at least once per year. To see the last inventory count per product, use the report .
You can do this the same way for all products and all locations, so you only carry out small inventory operations through the year, rather than a single large stock check at one point in the year (which usually turns out to be at an inconvenient time).